No They have no special significance All of these are simply used by convention to refer to a function For example, f(x)=e^x, a(x)=e^x, and z(x)=e^x all mean the same thing However, some notations mean only one thing For example, zeta(s) refers to the Riemann zeta function sum_(n=1)^oo1/n^s (See this link for more info Riemann zeta function) In general,Thus, f first translates x into I, if it is outside I, and otherwise, untranslates and computes g, if it is in I It follows that f (f (x)) = g (x) for all x outside I There are 2 R many such h's, and hence also this many f'sQED If g is continuous, then this f can be chosen also to be continuousF(x) = x 3 g(x) = x 5 defined for all real numbers (Note composite functions may have a different notation such as (f g)(x)) Q1) Solve the equation fg(x) = 27 Firstly, we must find the composite function fg(x) in terms of x before we solve it In order to do this, we can break down the function in the following way fg(x) = fg(x) = f(x5)
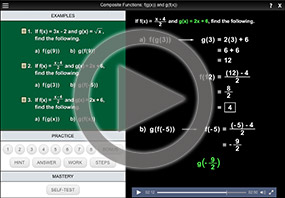
Composition Of Functions Composing Functions At Points
What does (f•g)(x) mean
What does (f•g)(x) mean-(a) For any constant k and any number c, lim x→c k = k (b) For any number c, lim x→c x = c THEOREM 1 Let f D → R and let c be an accumulation point of D Then lim x→c f(x)=L if and only if for every sequence {sn} in D such that sn → c, sn 6=c for all n, f(sn) → L Proof Suppose that lim x→c f(x)=LLet {sn} be a sequence in D which converges toc, sn 6=c for all nLet >0When you find (f o g)(x), there are two things that must be satisfied x must be in the domain of g, which means x is a real number (pretty easy to do) g(x) must be in the domain of f, which means that 1x 2 ^2 ≥ 4 (when you try to solve this, you get the empty set);



2
G (x) =2x or h (x) =2x,,,,,mean the same thing,,,except the axis is now g (x),,or h (x) The advantage of using functional notation is that different items can be differentiated, and still shown to be a function of x If we had a cost, we might use c (x) If we just used "c", it might not be clear that it is a function of xVertical Translation For the base function f (x) and a constant k, the function given by g (x) = f (x) k, can be sketched by shifting f (x) k units vertically Horizontal Translation For the base function f (x) and a constant k, the function given by g(x) = f (x k), can be sketched by shifting f (x) k units horizontally Vertical Stretches and ShrinksThe following rules apply to any functions f(x) and g(x) and also apply to left and right sided limits Suppose that cis a constant and the limits lim x!a f(x) and lim x!a g(x) exist (meaning they are nite numbers) Then 1lim x!af(x) g(x) = lim x!af(x) lim x!ag(x) ;
Therefore, we can conclude that A is open, meaning that its complement, {xf(x) ≤ g(x)} is closed (b) Let h X → Y be the function h(x)min{f(x),g(x)} Show that h is continuous Proof By a similar argument to that made in (a) above, we can show that B = {xg(x) ≤ f(x)} is closed Also, since f and g are continuous on X, it is true that In order to prove f(x) = O(g(x)), we need to find two positive constants, c and x 1, such that 0 ≤ f(x) ≤ cg(x) for all x ≥ x 1 We need to find values for c and x 1 such that the inequality holds What it means, is that past a certain point, a scaled version of g(x) will always be bigger than f(x) 6 Example 2*f(x) means two multiplied by the function f f(2x) means the function at 2x;
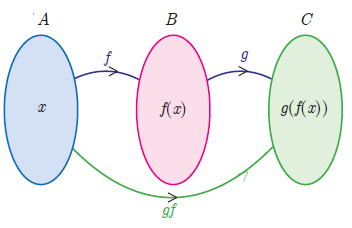
H(x) = f (x)g (x) h ( x) = f ( x) g ( x) Since f (x)gx f ( x) g x is constant with respect to f f, the derivative of f (x)gx f ( x) g x with respect to f f is 0 0 0 0 So what does this mean (f g)(x), the composition of the function f with g is defined as follows (f g)(x) = f(g(x)), notice that in the case the function g is inside of the function f Whereas in the composite(g f)(x), g(x) is the outside function and f(x) is the inside functionFor example, the function g (x) = f^ (1/2) (x) would be a function that satisfies g^2 (x) = f (x) Also, as a side note, the neutral function is more commonly called the identity function (and the neutral element 1 is called the identity element) (The trigonometric functions break this convention sin^2 (x) is taken to mean sin (x)*sin (x)




You Evaluated Functions Lesson 1 1 Perform Operations



Http People Math Sc Edu Binev Fall06 Q5s Pdf
1 Introduction The composition of two functions g and f is the new function we get by performing f first, and then performing g For example, if we let f be the function given by f(x) = x2 and let g be the function given by g(x) = x3, then the composition of g with f is called gf and is worked out(the limit of a sum is the sum of the limits) 2lim x!af(x) g(x$\begingroup$ Does "by definition" mean by the limit definition?



2




Calculus Cheat Sheet Derivatives Pauls Online Math Notes
The output f (x) is sometimes given an additional name y by y = f (x) The example that comes to mind is the square root function on your calculator The name of the function is \sqrt {\;\;} and we usually write the function as f (x) = \sqrt {x} On my calculator I input x for example by pressing 2 then 5 Then I invoke the function by pressingIf f(x) and g(x) are differentiable functions, then the derivative of the composition of g with f is where the notation g'(f(x)) means the function g'(x) evaluated at f(x) Once again, this result can be established from the definitionOr the value of the function evaluated at 2x Giving a name f to a function for the function using independant variable x will be named as f(x), to be read, "the function f of x" Shown alone, f and x are not factors, but are a complete name



Secure Media Collegeboard Org Apc Ap12 Calculus Ab Q4 Pdf



New Functions From Old
For f(x) into the formula for g(x) g(f(x)) = g p 4 x2 = 1 (p 4 x2)2 4 = 1 (4 x2) 4 = 1 2x Now, to nd the domain of (g f)(x), we consider both the domain of 1 2x and the domain of f(x) The domain of 1 2x includes every value except x= 0, and written in interval notation is (1 ;0)(0;1) The domain of f(x) = p 4 x2 is determined by nding where A more common notation is f = Θ (g (x)) (see wikipedia), but as the latter is a set of functions, a more settheoretical notation is to write f ∈ Θ (g (x)) instead It says that f belongs to a certain set of functions visàvis gThe Domain of g (x) = x2 is all the Real Numbers The composed function is (g º f) (x) = g (f (x)) = (√x)2 = x Now, "x" normally has the Domain of all Real Numbers but because it is a composed function we must also consider f (x), So the Domain is all nonnegative Real Numbers




Meaning Of Phi In Spivak S Proof Of Inverse Function Theorem Mathematics Stack Exchange




Key Concept 1 Example 1 Operations With Functions A Given F X X 2 2x G X 3x 4 And H X 2x 2 1 Find The Function And Domain For Ppt Download
$\endgroup$ – user Nov 21 '16 at 1656 $\begingroup$ Ahh, my bad!• Constant Multiple Rule g(x)=c·f(x)theng0(x)=c·f0(x) • Power Rule f(x)=x n thenf 0 (x)=nx n−1 • Sum and Difference Rule h(x)=f(x)±g(x)thenh 0 (x)=f 0 (x)±g 0 (x) Problem Assume that f has a derivative everywhere Set g(x)=xf(x) Using the definition of the derivative, show that g has a derivative and that g'(x)=f(x)xf'(x) What I know I know the definition of the derivative is f(xh)f(x)/h I don't know how to plug it



Ehrman Weebly Com Uploads 5 7 6 4 Continuity Hw Part 1 Solutions Pdf
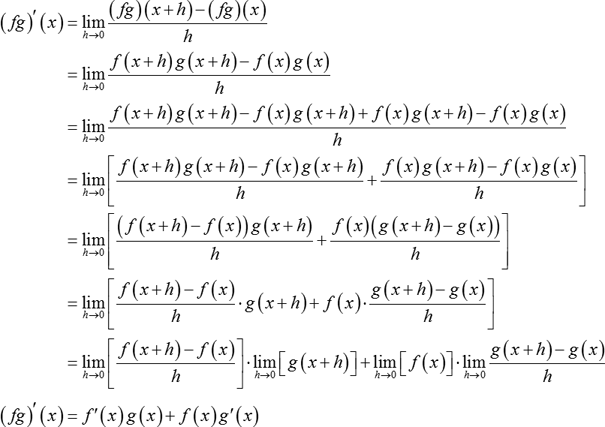



Definition Of Product Rule Chegg Com
G*(x)(4*f*(x))=0 Step 1 Pulling out like terms 11 Pull out like factors gx 4xf = x • (g 4f) Equation at the end of step 1 Step 2 Theory Roots of a product 21 A product of several terms equals zero When a product of two or more terms equalsFinally, for any set X of variables, the set G(X) of guarded functional terms with respect to X is the set of functional terms where each occurrence of a variable not in X is in the scope of one and only one functional symbol of F and each occurrence of a variable in X is in the scope of at most one functional symbol of F This set is defined by – X ⊆ G(X), EG ⊆ G(X),Definition (sum and product) Let f and g be functions from a set A to the set of real numbers R Then the sum and the product of f and g are defined as follows For all x, ( f g)(x) = f(x) g(x) , and for all x, ( f*g)(x) = f(x)*g(x) , where f(x)*g(x) is the product of two real numbers f(x) and g(x) Example Let f(x) = 3x 1 and g(x) = x 2




What Is The Meaning Of A Small O In Between Function Names I E F O G Mathematics Stack Exchange




Adding Limits In La Tex Tex Latex Stack Exchange
In this video we learn about function composition Composite functions are combinations of more than one function In this video we learn about f(g(x)) and gFind two linear functions f(x) and g(x) such that the product h(x) = f(x)g(x) is tangent to each This problem was posed by a group of teachers during a workshop in which the use of function graphers was being explored Our analysis is presented as a sort of stream of consciousness account of how one might explore the problem with the tools atF (x)g (x)=f (x) G (x)F (x) g (x) Divide both sides by f (x)g (x), and write g=G' and f'=F' to get 1=G/G' F/F' Now clearly some exponential functions for G and F can be chosen for this to hold




Chapter 4 Arithmetic In F X Polynomial Arithmetic And The Division Algorithm Pdf Free Download
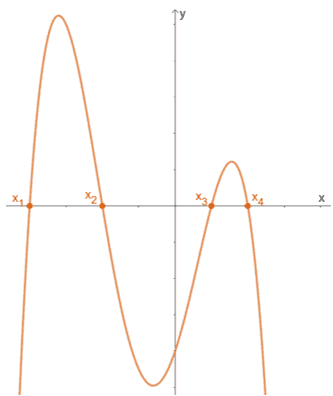



Zeros Of A Function Explanation And Examples
The equation is in standard form gx=12 g x = − 1 2 Divide both sides by g Divide both sides by g \frac {gx} {g}=\frac {12} {g} g g x = g − 1 2 Dividing by g undoes the multiplication by g Dividing by g undoes the multiplication by gYes I have to show it by the limit definition $\endgroup$ – JoakimSjo Nov 21 '16 at 1657First, the function 5x^22 is performed, and then the result is squared The inside function is performed first, and the outside function is performed second So if f (g (x))= (5x^22)^2, then one possibility could be g (x)=5x^22 for the inside function, and f (x)=x^2 for the outside function
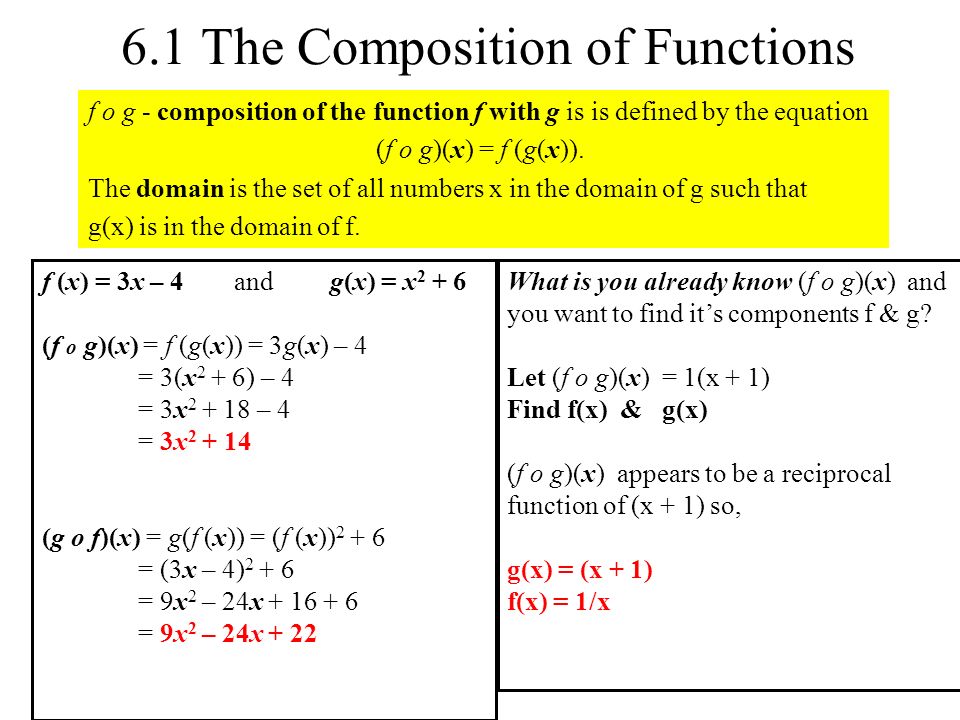



6 1 The Composition Of Functions F O G Composition Of The Function F With G Is Is Defined By The Equation F O G X F G X The Domain Is The Set Ppt Download




Operations On Functions Precalculus Section 1 4
F (x) is a function g from the reals to the reals, whose domain is the set of the reals x, such that f(x) ≠ 0 The range of a function is the set of the images of all elements in the domain However, range is sometimes used as a synonym of codomain, generally in old textbooksIf f (x) = g1 (x), then g (f (x)) = x By definition, if we plug the inverse of a function into that function, then the result is x We are given that See full answer belowDefinition (bigoh) Let f and g be functions from the set of integers (or the set of real numbers) to the set of real numbers Then f (x) is said to be O( g(x) ), which is read as f (x) is bigoh of g(x) , if and only if there are constants C and n 0 such that f(x) C g(x) whenever x > n 0 Note that bigoh is a binary relation on a set of functions (What kinds of properties does it



Explore Properties Of An Alternative Definition Of The Derivative Stumbling Robot




Given The Definition Of F X And G X Below Find The Value Of F G 1 Brainly Com
If y = f(x) g(x), then dy/dx = f'(x) g'(x) Here's a chance to practice reading the symbols Here's a chance to practice reading the symbols Read this rule as if y is equal to the sum of two terms or functions, both of which depend upon x, then the function of the slope is equal to the sum of the derivatives of the two terms4 If argmax f(x) >0, then argmaxf(x) = argmin 1 f(x) 5 If gis strictly monotonic, meaning that > implies g( ) >g( ), then argmaxg(f(x)) = argmaxf(x) The last property is used frequently when doing calculations involving probabilities, since the logarithm (aAnd "( f o g)(x)" means "f (g(x))" That is, you plug something in for x, then you plug that value into g, simplify, and then plug the result into f The process here is just like what we saw on the previous page, except that now we will be using formulas to find values, rather than just reading the values from lists of points Given f(x) = 2x 3 and g(x) = –x 2 5, find (g o f)(1)




The Functions F And G Are Defined By Find F X And Chegg Com
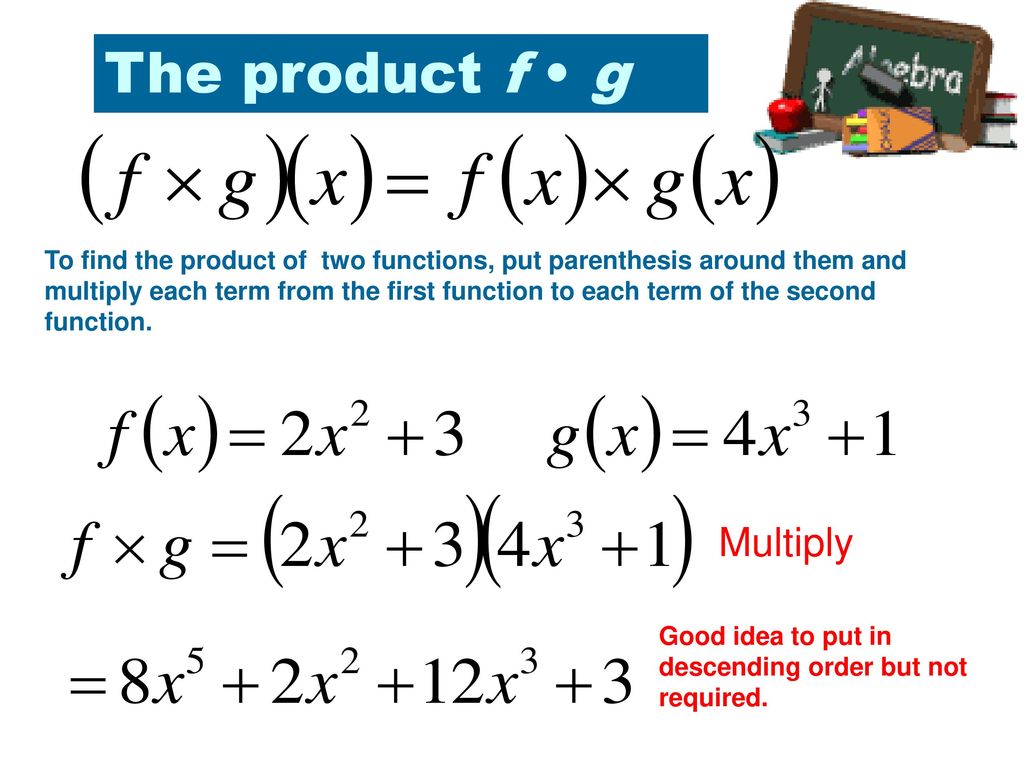



Section 1 5 Combinations Of Functions Ppt Download
Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with stepbystep explanations, just like a math tutorGiven f (x) = 3x 2 and g(x) = 4 – 5x, find (f g)(x), (f – g)(x), (f × g)(x), and (f / g)(x) To find the answers, all I have to do is apply the operations (plus, minus, times, and divide) that they tell me to, in the order that they tell me toIn simple terms, that notation implies that f^1 (x) is the Inverse Function to f (x) To make is a bit easier to wrtie, let's let g (x) be the inverse of f (x), in other words, g (x) = f^1 (x) In terms of mappings, If D is the domain of f and R is the Range of f, then




Solved By Definition F Circ G X So If G 2 5 And F 5 12 Then F Circ G 2



2
In mathematics, function composition is an operation that takes two functions f and g and produces a function h such that h(x) = g(f(x)) In this operation, the function g is applied to the result of applying the function f to x That is, the functions f X → Y and g Y → Z are composed to yield a function that maps x in X to g(f(x)) in Z #2 the letter which you use to label a function has no special meaning g (x) just identifies a function of x, in the same way as that f (x) does Using a "g" instead of an "f" only means the function has a different label assigned to it Typically this is done where you have already got an f (x), so creating another one would beF (x) and g (x) are functions f typically models the time an algorithm takes to work on an input of size x When we say f (x) = O (g (x)), what we mean is approximately "the time taken by the algorithm to work on an input of size x grows no more quickly than a multiple of g (x) for sufficiently large x"
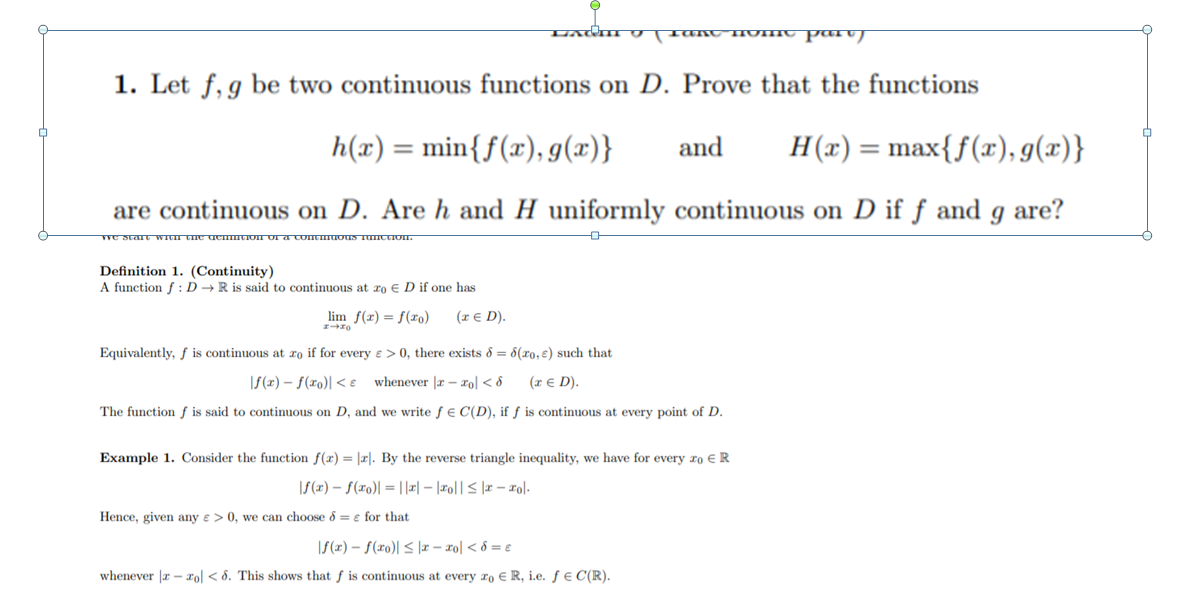



Know That H X Min F X G X Chegg Com



Http Www Csun Edu Ac Courses Math512a Hmwk9 Sol 512a Pdf
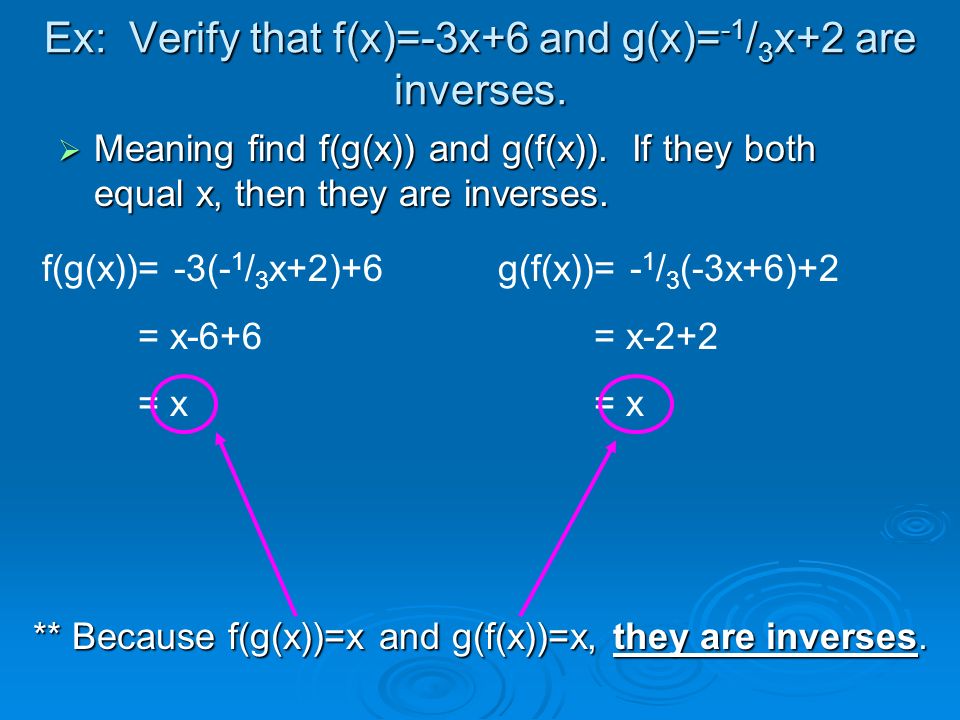
Answer The answer is (d) f(g(x)) = x and g(f(x)) = x Stepbystep explanation We are to select the correct statement that verifies the functions f(x) and g(x) are inverses of each other We know that if f(x) is the inverse of g(x), then we write If g(x) is the inverse of f(x), then we write So, we can writeWhen you combine the two domains to see what they have in common, you find the intersection of everything and nothing is The functions f(x) and g(x) are defined as f(x) = 3x 1 and g(x) = 4x 2 fog(x) = f(g(x)) = f(4x 2 ) = 3(4x 2) 1 = 12x 6 1 = 12x 7 fog(0) = 12*0 7 = 7




Functions 1 Definition Of A Function A Function



Http Aubg Edu Documents 248
We also have ∀ x in the domain h ( x) = x by definition, and that means every x is a fixpoint of h (this is trivially true for any identity) The language borrowed from category theory is that f is a retraction of g, and g is a section of f If f is both a retraction and a section of g, then it's called an inversionFind (f g)(x) for f and g below f(x) = 3x 4 (6) g(x) = x2 1 x (7) When composing functions we always read from right to left So, rst, we will plug x into g (which is already done) and then g into f What this means, is that wherever we see an x in f we will plug in g That is, g acts as our new variable and we have f(g(x)) 1A composite function is generally a function that is written inside another function Composition of a function is done by substituting one function into another function For example, f g (x) is the composite function of f (x) and g (x) The composite function f g (x) is read as "f of g of x " The function g (x) is called an inner



2



Www Westada Org Site Handlers Filedownload Ashx Moduleinstanceid 8684 Dataid Filename Task 3 6 Pdf
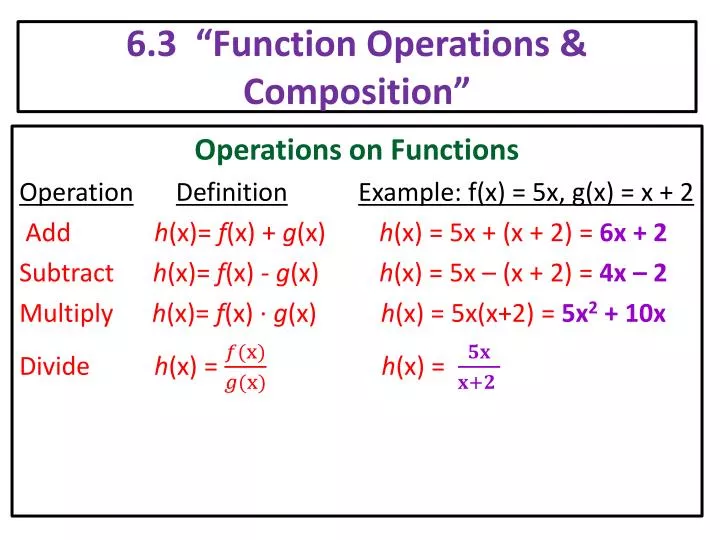



Ppt 6 3 Function Operations Composition Powerpoint Presentation Id
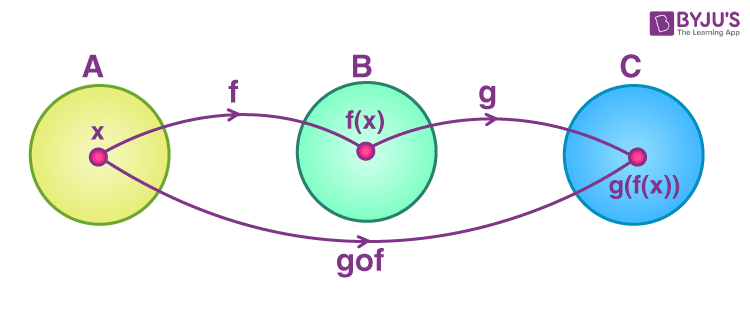



Composition Of Functions Definition Properties And Examples



Www Math Tamu Edu Shatalov 2 Section 5 1 5 4 F18 Pdf




Function Mathematics Wikipedia
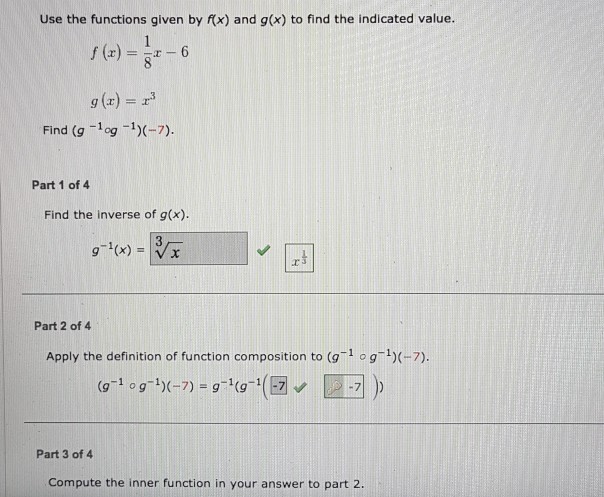



Use The Functions Given By Fx And G X To Find The Chegg Com



Http Www Math Umd Edu Immortal Math115 Sect2 78 Ln Pdf



What Does Max F X G X Mean Quora




Taste Of Haskell Definition Of Composition Stack Overflow




1 Points Details Ghcolalg12 3 4 072 1 Let F X 1 X 3 And G X Homeworklib




Composition Of Functions Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Inverse Functions Definition A Function Is A Set Of Ordered Pairs With No Two First Elements Alike F X X Y 3 2 1 4 7 6 9 12 Ppt Download




The Limit Laws



Composition Of Function Chilimath




Function Mathematics Wikipedia



Http Maths Dur Ac Uk Dma0wjz B1 Anlec1 Pdf



Composite Functions F G X And G F X Youtube



Composition And Inverse Of Functions



How To Find The Missing Value In Composition Of Two Functions




Why Polynomial Functions F X G X F G X Mathematics Stack Exchange




Function Operation Definition Overview Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




You Evaluated Functions Lesson 1 1 Perform Operations




Oneclass If Functions F X And G X Are Continuous For 0 X 4 Could The Function F X G X Possibly




Definition Of The Bijection F From Theorem 2 The Dyck Path X Has 4 Download Scientific Diagram
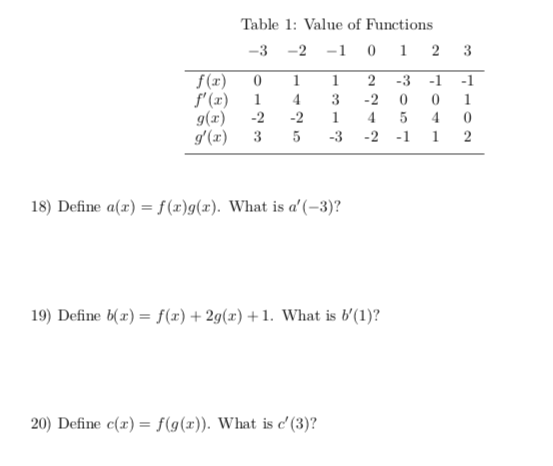



Solved F X F X G X G X Table 1 Value Of Functions Chegg Com
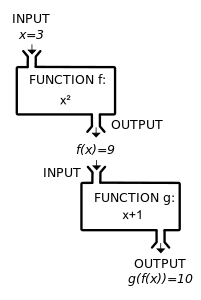



Function Mathematics Wikipedia



View Question What Is The Solution To F X G X




Proof Of The Quotient Rule



Q Tbn And9gcq3k4crna5aowbckdwotcepc7srb Ubkhdcqsvwzwhqp8plminb Usqp Cau




The Algebra Of Functions



4 8 L Hopital S Rule Calculus Volume 1




Proof Of The Product Rule




Answered Use The Pair Of Functions To Find Bartleby




5 If F Is A Differentiable Function And Gx Xfx Gauthmath




Composite Function Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Http Fsw01 c Cuny Edu Luis Fernandez01 Web Texts Representationtheoryln Pdf



Composition Of Functions What Does F G X Mean Youtube



Gx Generic By Acronymsandslang Com



2




Derivative Rules Mth 124 Survey Of Calculus I Docsity



2




2 6 Combining Functions Flashcards Quizlet



7 4 Logarithmic Differentiation



Explore Properties Of An Alternative Definition Of The Derivative Stumbling Robot




The Functions F And G Are Defined As F X X 6 G X Chegg Com



Composite Functions
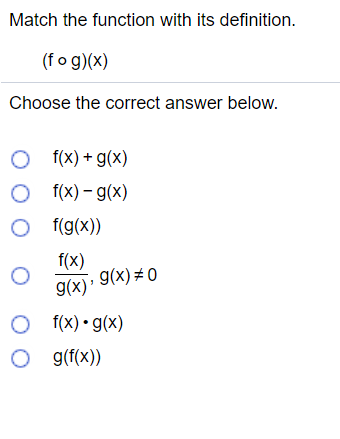



Match The Function With Its Definition Fog X Chegg Com



0 Divided By 0 Article About 0 Divided By 0 By The Free Dictionary




Composition Of Functions Composing Functions At Points



Http Mrsalter Weebly Com Uploads 2 2 9 4 Ap Calc 2 3 Ws Answers Pdf




Composition Of Functions Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Inverse Functions Given 2 Functions F X G X If F G X X And G F X X Then F X G X Are Inverses Of Each Other Symbols F 1 X Means F Ppt Video Online Download



Solved Given F X 2x 4 And G X 1 2 2 Use The Definition Of Inverses To Determine If F And G And Inverses Course Hero
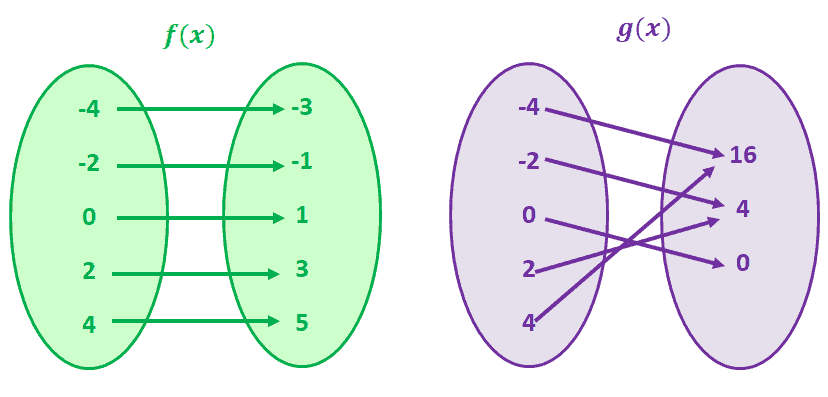



One To One Function Explanation Examples




To Define Function And Introduce Operations On The Set Of Functions To Investigate Which Of The Field Properties Hold In The Set Of Functions Pdf Free Download



Q Tbn And9gcri3fpyfvwyir3valez Far1ibhtlhp8jst3ktwyrvxbdne454c Usqp Cau



2
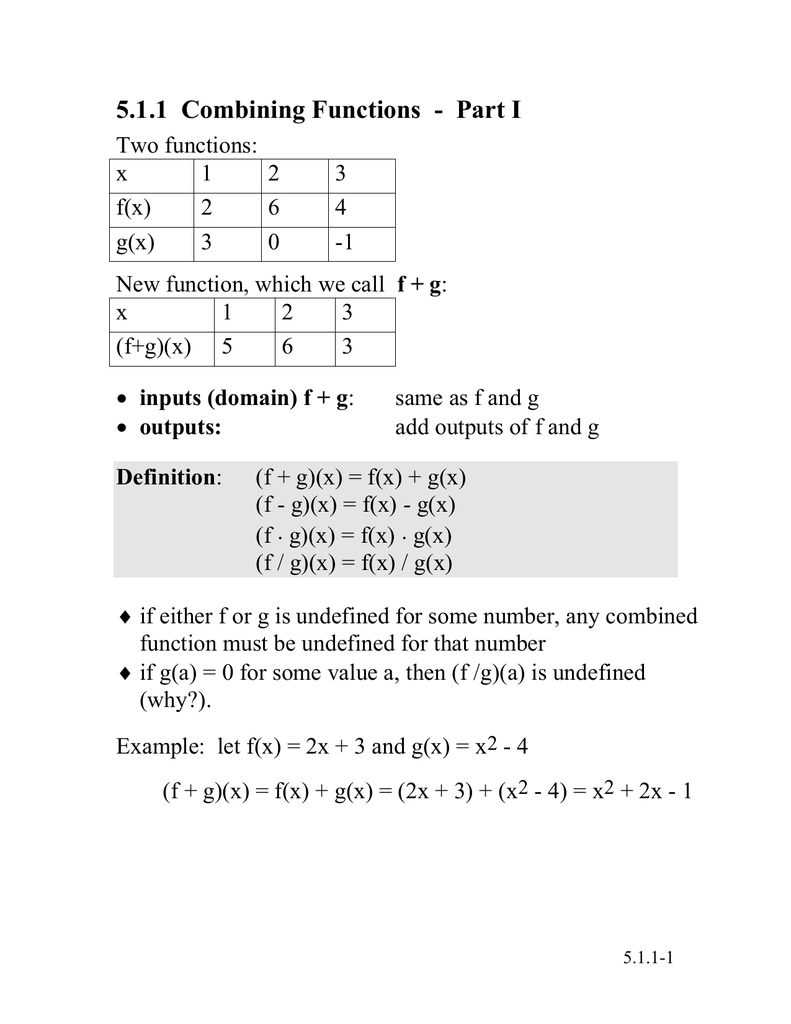



5 1 1 Combining Functions Part I




Review Relation A Mapping Of Input Values X Values Onto Output Values Y Values Here Are 3 Ways To Show The Same Relation Y X 2 X Y Ppt Download
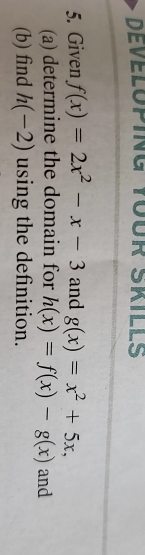



Given Math F X 2x 2 X 3 Math And Math G X X 2 5x Math A Determine The Domain For H X F X G X And B Find H 2 Using The Definition Homework Help And Answers Slader
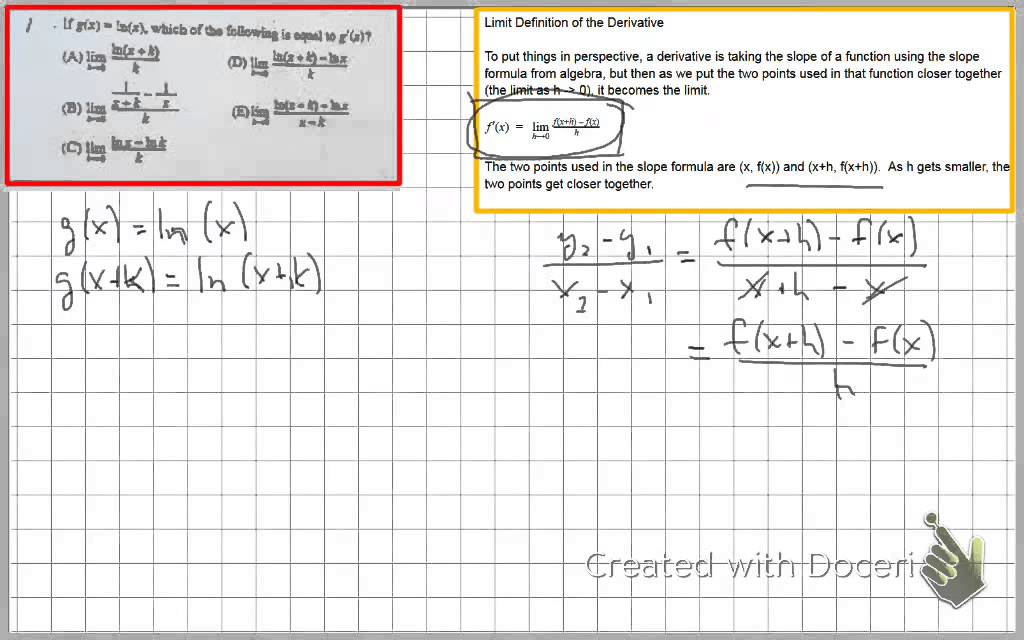



Calculus If G X Ln X What Is G X Youtube




By Dr Julia Arnold The Algebra Of Functions What Does It Mean To Add Two Functions If F X 2x 3 And G X 4x 2 What Would F G X Be




Composing Functions Article Khan Academy



Http Citeseerx Ist Psu Edu Viewdoc Download Doi 10 1 1 3 73 Rep Rep1 Type Pdf




Use The Definition Of Inverses To Determine Whether Fand G Are Inverses 1 F X 5x Homeworklib




1 6 Function Operations And Composition Of Functions Domain Of A Function Function Mathematics



2



Faculty Math Illinois Edu Aydin Math2 Lecturenotes M2 Sec1 4 Pdf



Efisd Net Common Pages Displayfile Aspx Itemid




Calculus Cheat Sheet All




Answered A Use The Definition Of F To Show Bartleby




1 6 Function Operations And Composition Of Functions Domain Of A Function Function Mathematics



Http Homepages See Leeds Ac Uk Eargah Ears1160 Lecture1 Pdf



2



1




How To Differentiate 2x 1 X 3 Using The Quotient Rule



Secure Media Collegeboard Org Apc Ap12 Calculus Ab Q4 Pdf



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿